Advancing Sustainable Energy: How Large-Scale Continuous Furnaces Transform the Charcoal Production Plant Industry
In the modern world, industries are rapidly shifting toward cleaner, more sustainable methods of energy production. Among the most efficient technologies driving this transformation is the large-scale continuous furnace, a breakthrough innovation redefining how charcoal is produced worldwide. Combined with a well-integrated charcoal production plant, this technology enables efficient carbonization of biomass while minimizing waste and emissions. From environmental sustainability to economic efficiency, continuous furnaces have become a cornerstone of modern biomass processing.
Understanding the Role of Large-Scale Continuous Furnaces
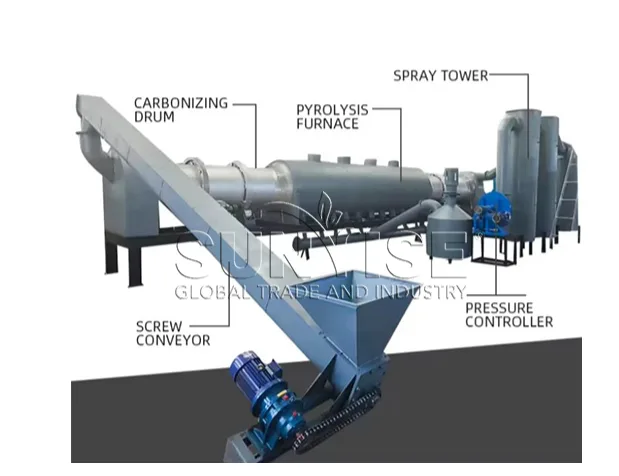
Traditionally, charcoal production relied on batch kilns—small, manually operated setups that burned wood or agricultural residues in limited cycles. These methods were slow, labor-intensive, and environmentally harmful due to uncontrolled smoke and heat loss. In contrast, large-scale continuous furnaces represent the evolution of charcoal technology. They enable nonstop carbonization, allowing raw materials to enter one end and finished charcoal to exit the other without interruption.
The continuous process ensures steady production, consistent product quality, and higher energy efficiency. Inside the furnace, biomass undergoes controlled pyrolysis—a process where organic material decomposes at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. This transformation releases volatile gases, leaving behind high-carbon charcoal suitable for industrial, domestic, and agricultural use.
What makes these furnaces “large-scale” is their ability to handle tons of biomass per day. They are equipped with advanced temperature control systems, automatic feeding and discharge mechanisms, and efficient heat recovery designs. The result is a streamlined operation capable of producing charcoal with stable carbon content and uniform particle size—ideal for commercial applications.
The Heart of Every Modern Charcoal Production Plant
A charcoal production plant is more than just a single furnace. It is an integrated system where multiple processes—crushing, drying, carbonization, cooling, and briquetting—work in harmony. At the core of this setup lies the large-scale continuous furnace, responsible for the actual conversion of biomass into charcoal.
Here’s a simplified overview of how a modern charcoal production plant operates:
- Raw Material Preparation: Biomass such as wood chips, coconut shells, bamboo, or agricultural waste is first crushed to a uniform size. Proper sizing ensures smooth feeding into the furnace and even heating during carbonization.
- Drying Process: Moisture content plays a critical role in charcoal quality. The raw materials are dried to a moisture level below 15% before entering the furnace, improving thermal efficiency and reducing energy waste.
- Continuous Carbonization: Inside the furnace, the prepared biomass is slowly heated in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. The process drives off volatile gases and transforms the material into high-quality charcoal.
- Cooling and Discharging: The charcoal exits the furnace at high temperatures and is immediately cooled to prevent oxidation. This step preserves the integrity and fixed carbon content of the product.
- Briquetting and Packaging: For commercial use, the charcoal may be compressed into uniform briquettes, which are easier to transport, store, and sell.
Each of these stages contributes to the overall performance and productivity of the plant. Together, they form a continuous, automated process that minimizes manual labor, improves efficiency, and enhances product uniformity.
Benefits of Using Large-Scale Continuous Furnaces in Charcoal Production
1. Higher Efficiency
Large-scale continuous furnaces eliminate downtime associated with batch systems. They can operate 24/7, allowing constant feeding and discharge. The result is a dramatic increase in production output and energy savings.
2. Consistent Charcoal Quality
The precise control of temperature and residence time ensures uniform carbonization. This consistency is essential for industries that rely on specific charcoal grades, such as metallurgy, filtration, or barbecue production.
3. Environmental Sustainability
Modern furnaces are designed to capture and reuse the gases released during carbonization. These gases are burned to provide heat for the system, reducing fuel consumption and minimizing emissions. This closed-loop design makes the technology far more eco-friendly than traditional kilns.
4. Reduced Labor and Maintenance Costs
Automation in feeding, carbonization, and cooling reduces the need for manual handling. The sturdy design and continuous operation also mean fewer maintenance interruptions.
5. Adaptability to Various Raw Materials
Whether the input is wood chips, rice husks, coconut shells, or bamboo, a continuous furnace can be adjusted to handle different feedstocks without compromising efficiency.
Economic Impact and Global Demand
The rising global demand for eco-friendly fuel sources has made charcoal production a lucrative industry. Countries across Asia, Africa, and South America are adopting charcoal production plants equipped with large-scale continuous furnaces to meet domestic and export needs. The ability to produce charcoal continuously allows operators to maintain stable supply chains and respond quickly to market demand.
Furthermore, the byproducts of carbonization—such as wood vinegar, tar, and combustible gases—can be collected and refined for additional profit. These secondary outputs enhance the overall economic value of the production process, making the investment in continuous furnaces even more rewarding.
Sustainability and the Future of Charcoal Production
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt large-scale continuous furnaces is sustainability. As nations seek alternatives to fossil fuels, biochar and charcoal derived from renewable biomass are gaining importance. These products can sequester carbon, enrich soil, and serve as cleaner fuels. By integrating modern carbonization technology, industries can play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
In addition, many governments are tightening environmental regulations for traditional charcoal kilns. The cleaner operation and reduced pollution from continuous furnaces make them the ideal choice for businesses aiming to comply with new standards while maintaining profitability.
Conclusion
The future of charcoal production lies in innovation, automation, and sustainability. Large-scale continuous furnaces are revolutionizing the industry by offering high efficiency, superior product quality, and environmentally responsible operation. When combined with a fully equipped charcoal production plant, they create a powerful system capable of meeting global demand for renewable carbon products.
Whether for industrial applications or household fuel, modern charcoal production technologies ensure that we move toward a cleaner, greener, and more efficient energy landscape—proving that progress and sustainability can indeed go hand in hand.