How to Choose the Best Firewood for Your Log Burner
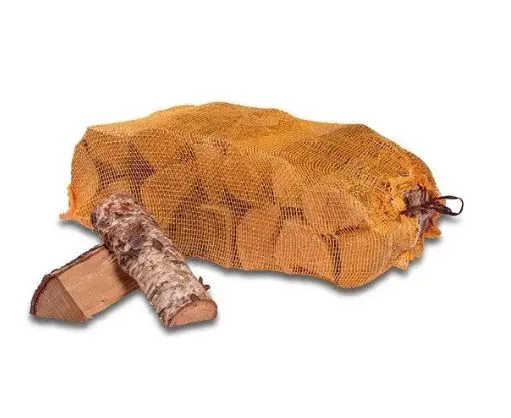
Selecting the right firewood for your log burner is crucial for maximizing heat output, minimizing maintenance, and ensuring safe operation. With numerous options available in the market, understanding the characteristics of different wood types, moisture content requirements, and quality indicators will help you make an informed decision. Kiln dried logs represent the premium choice for discerning homeowners who demand consistent performance and efficiency from their heating systems.
The quality of your firewood directly impacts everything from ignition speed to burn duration, smoke production, and even the longevity of your log burner. Poor quality wood can lead to excessive creosote buildup, reduced heat output, and increased maintenance requirements. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential factors to consider when choosing firewood, ensuring you get the maximum return on your investment while keeping your home warm and comfortable.
Understanding Different Types of Firewood
When selecting firewood for your log burner, the fundamental distinction lies between hardwoods and softwoods, each offering unique burning characteristics and applications. Hardwoods, derived from deciduous trees, provide dense wood fibers that burn longer and produce more heat per unit volume compared to their softwood counterparts.
Premium hardwood varieties include oak, birch, beech, ash, sycamore, and chestnut, each bringing distinct qualities to your burning experience. Oak stands out as one of the most popular choices due to its exceptional density and long burning time, making it ideal for overnight heating. Birch offers excellent heat output with attractive flame patterns, while ash is renowned for its ability to burn well even when relatively fresh. Beech provides steady, consistent heat with minimal sparking, and sycamore offers good heat output with clean burning characteristics.
Softwoods, primarily from coniferous trees like larch and spruce, serve different purposes in your log burner strategy. While they may not burn as long as hardwoods, they ignite more easily and burn hotter initially, making them excellent for kindling and quick heat generation. Larch, in particular, is considered one of the premium softwoods due to its higher density compared to other conifers, while spruce provides rapid ignition and is excellent for getting fires started quickly.
The choice between hardwood and softwood often depends on your specific heating needs and burning patterns. Many experienced log burner users employ a mixed approach, using softwoods for initial ignition and quick heat boosts, then transitioning to hardwoods for sustained, long-term heating.
Why Kiln Dried Logs Are the Premium Choice
Kiln dried logs represent the pinnacle of firewood quality, offering superior performance characteristics that justify their premium positioning in the market. The kiln drying process involves carefully controlled heating in specialized chambers, reducing moisture content to below 20 percent, which significantly exceeds the performance of naturally seasoned alternatives.
The controlled drying environment ensures consistent quality across every log, eliminating the variables that affect traditionally seasoned wood. This process not only removes excess moisture but also eliminates insects, fungi, and other potential contaminants that can affect both storage and burning characteristics. The result is cleaner burning wood that produces more heat, less smoke, and minimal creosote buildup in your chimney system.
From an efficiency standpoint, kiln dried logs ignite more readily and burn more completely than higher moisture alternatives. The reduced water content means more energy goes toward heat production rather than moisture evaporation, resulting in significantly better heat output per unit of wood. This efficiency translates directly into cost savings, as you require less wood to achieve the same heating results.
The environmental benefits of kiln dried logs extend beyond their burning characteristics. Many kiln drying operations utilize renewable biomass energy sources, creating a sustainable production cycle. Additionally, the improved burning efficiency means reduced particulate emissions, contributing to better air quality both inside and outside your home.
Storage advantages also make kiln dried logs attractive for homeowners with limited space. The reduced moisture content means lighter weight per unit volume, making handling easier while also reducing the risk of mold or decay during storage periods.
Hardwood vs Softwood: Making the Right Selection
Understanding when to use hardwood versus softwood firewood requires consideration of your heating patterns, log burner characteristics, and personal preferences. Each wood type serves distinct purposes in an optimal burning strategy, and the best approach often involves strategic use of both categories.
Hardwoods excel in situations requiring sustained, consistent heat output over extended periods. Their dense fiber structure creates long-lasting coals that continue producing heat long after the visible flames diminish. This characteristic makes hardwoods ideal for overnight burning, maintaining warmth throughout cold winter nights without frequent refueling. The slower burning rate also means less frequent attention is required, allowing you to enjoy your fire without constant management.
Mixed hardwood combinations offer particular advantages, as different species complement each other’s burning characteristics. Oak provides the foundation with long burning times, while birch adds visual appeal with bright flames. Ash contributes easy ignition properties, and beech offers steady, consistent heat production. This diversity ensures optimal performance across various burning conditions and user preferences.
Softwoods serve crucial roles in fire management and specific heating scenarios. Their lower density and resinous content mean they ignite quickly and burn with intense heat, making them perfect for rapid room warming or fire establishment. Larch and spruce, the premium softwood options, provide better heat output and longer burning times than other coniferous species while maintaining the quick-ignition characteristics that make softwoods valuable.
The seasonal variation in your heating needs may also influence your hardwood versus softwood selection. During shoulder seasons when occasional heating is required, softwoods provide quick warmth without the commitment of long-burning hardwoods. Conversely, during peak winter months, hardwoods become essential for maintaining consistent comfort levels throughout your home.
Moisture Content: The Critical Factor for Efficiency
Moisture content stands as the single most important factor determining firewood quality and performance in your log burner. Understanding how moisture levels affect burning characteristics, efficiency, and safety will help you make informed purchasing decisions and optimize your heating experience.
Properly dried firewood should contain moisture levels below 20 percent, with premium kiln dried options often achieving moisture contents between 10 and 15 percent. This low moisture threshold ensures efficient combustion, as excessive water content forces your log burner to spend valuable energy evaporating water rather than producing heat for your home. Wood with moisture content above 25 percent will struggle to maintain combustion and produce significantly less heat output.
The relationship between moisture content and ignition characteristics becomes immediately apparent when comparing different wood qualities. Dry wood ignites readily with minimal effort, establishing strong flames that spread quickly throughout the log. Wet wood, conversely, resists ignition, produces excessive smoke, and often results in incomplete combustion that creates creosote deposits in your chimney system.
Heat output varies dramatically with moisture content changes. Studies indicate that reducing moisture content from 30 percent to 20 percent can increase heat output by up to 25 percent, while further reduction to 15 percent provides additional efficiency gains. This improved performance directly translates into reduced fuel consumption and lower heating costs over the course of a heating season.
Environmental implications of moisture content extend beyond your immediate heating efficiency. Wet wood produces significantly more particulate emissions and contributes to air quality degradation. Properly dried wood burns more completely, reducing harmful emissions while providing better indoor air quality for your family.
Testing moisture content in your firewood requires a moisture meter, an inexpensive tool that provides accurate readings when inserted into freshly split wood surfaces. Regular testing ensures you maintain quality standards and can identify potential issues before they affect your burning experience.
Sourcing and Sustainability Considerations
Responsible sourcing of your firewood supports environmental sustainability while ensuring long-term availability of quality wood supplies. Understanding sustainable forestry practices and selecting suppliers who prioritize environmental responsibility contributes to forest health and ecosystem preservation.
Sustainable harvesting practices focus on selective cutting methods that maintain forest diversity and regeneration capacity. Quality suppliers source their wood from managed forests where harvesting supports overall forest health through careful removal of mature trees, creating space for younger growth while maintaining ecosystem balance. This approach ensures continuous wood supplies without compromising long-term forest sustainability.
Local sourcing provides multiple benefits beyond environmental considerations. Reduced transportation distances minimize carbon footprints while supporting regional economies and forest management practices. Local suppliers often provide better customer service, including delivery flexibility and ongoing support for your firewood needs. Additionally, locally sourced wood is typically better adapted to your regional burning conditions and climate requirements.
Certification programs help identify responsibly sourced firewood options. Look for suppliers who participate in recognized forestry certification schemes that verify sustainable harvesting practices, environmental protection measures, and chain of custody documentation. These certifications provide assurance that your firewood purchase supports responsible forest management.
The kiln drying process itself can contribute to sustainability when powered by renewable energy sources. Many premium suppliers utilize biomass energy systems that burn wood waste to power their kiln operations, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes external energy requirements while processing wood waste into useful energy.
Quality suppliers maintain transparent operations, providing information about wood sources, processing methods, and sustainability practices. They should be able to discuss their harvesting areas, rotation schedules, and environmental protection measures, demonstrating commitment to long-term forest health and sustainable business practices.
Storage and Handling Best Practices
Proper storage and handling techniques preserve firewood quality, extend usable life, and ensure optimal performance in your log burner. Even premium kiln dried logs can deteriorate without appropriate storage conditions, making these practices essential for protecting your investment.
Covered storage areas provide essential protection from precipitation while allowing adequate air circulation to maintain dry conditions. Purpose-built log stores or simple roof structures shield your wood from rain and snow while preventing moisture reabsorption that can compromise burning performance. The storage area should provide protection from direct weather exposure while avoiding completely enclosed spaces that can trap moisture and promote mold growth.
Ground contact represents one of the primary threats to stored firewood quality. Elevating your wood stack using pallets, treated lumber, or commercial log storage systems prevents ground moisture wicking and reduces pest access. This elevation also improves air circulation underneath the stack, promoting continued drying and preventing decay from ground contact.
Stacking techniques influence both storage efficiency and wood preservation. Proper stacking allows air circulation between logs while providing structural stability for safe access. Cross-stacking at stack ends provides stability, while maintaining consistent spacing between logs promotes air movement throughout the pile. Avoid tight stacking that restricts airflow, as this can create conditions conducive to mold growth and moisture retention.
Bulk bag storage offers convenience for homeowners with limited storage space or those preferring ready-to-use packaging. Extra large bulk bags provide substantial quantities while maintaining clean, organized storage that’s easy to access and manage. These bags protect wood from contamination while allowing drainage and air circulation when properly positioned.
Rotation practices ensure you use older stock first, preventing deterioration from extended storage periods. Even properly dried and stored wood can gradually lose quality over extended periods, making rotation important for maintaining optimal performance. Mark storage areas or bags with purchase dates to facilitate proper rotation and ensure consistent wood quality.
Getting the Most from Your Log Burner
Maximizing your log burner’s performance requires understanding proper firing techniques, maintenance practices, and fuel management strategies that work synergistically with quality firewood selection. These practices ensure safety, efficiency, and longevity for both your wood supply and heating equipment.
Fire establishment techniques set the foundation for optimal burning performance throughout your heating session. Begin with proper kindling materials, including natural firelighters or wood wool options that ignite reliably without chemical accelerants. Build your initial fire using smaller pieces of dry softwood that ignite quickly and establish strong heat levels before adding larger hardwood logs for sustained burning.
Air control management becomes crucial once your fire is established. Modern log burners provide precise air control systems that regulate combustion intensity and efficiency. Understanding how to adjust these controls based on your wood type, desired heat output, and burning phase ensures optimal performance while preventing excessive fuel consumption or incomplete combustion.
Loading techniques influence both safety and efficiency in your log burner operation. Add new logs before existing fuel is completely consumed, maintaining consistent heat levels without temperature fluctuations that waste energy and reduce comfort. Position logs to promote even burning and adequate air circulation, avoiding overpacking that restricts airflow and reduces combustion efficiency.
Regular maintenance practices keep your log burner operating safely and efficiently throughout the heating season. Clean ash removal prevents airflow restriction while regular chimney inspection and cleaning prevent dangerous creosote buildup that can result from poor quality or improperly burned wood. Quality kiln dried logs significantly reduce maintenance requirements by burning more completely and producing less creosote formation.
Fuel planning ensures consistent heating availability throughout the season while taking advantage of bulk purchasing opportunities. Calculate your seasonal wood requirements based on your home’s heating needs, log burner efficiency, and desired comfort levels. Purchase quality wood early in the season to ensure availability and allow for proper storage establishment before peak heating demands begin.
Conclusion
Choosing the best firewood for your log burner involves balancing multiple factors including wood type, moisture content, sustainability, and storage considerations. Kiln dried logs emerge as the premium choice for homeowners seeking maximum efficiency, convenience, and environmental responsibility in their heating fuel selection.
The investment in quality firewood pays dividends through improved heat output, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced safety in your log burner operation. By understanding the characteristics of different wood types, maintaining proper storage practices, and implementing effective burning techniques, you can maximize both performance and satisfaction from your log burner heating system.
Remember that quality firewood represents just one component of an effective heating strategy. Combine premium fuel selection with proper equipment maintenance, efficient burning practices, and appropriate storage techniques to achieve optimal results from your log burner investment. The warmth, comfort, and ambiance provided by a well-managed wood heating system, fueled by quality kiln dried logs, creates lasting value for your home and family throughout the heating season.