Air Permeability Test Unit

The Air permeability test unit is a critical aspect of evaluating the airflow properties of fabrics and other porous materials. It is essential for industries that rely on precise control of air movement, including apparel, industrial textiles, medical applications, and technical products like filters. Understanding the standard units used in air permeability testing, the air permeability formula, and their role in analyzing fabric performance is vital for manufacturers, designers, and quality control professionals.
What is Air Permeability?
Air permeability refers to the ability of a material to allow air to pass through it under specific conditions. It is influenced by factors such as fabric construction, thickness, fiber type, and finishing treatments. The results of an air permeability test are expressed in specific units, which help quantify the material’s breathability or resistance to airflow.
This property is particularly important in applications where breathability, thermal insulation, or air filtration efficiency plays a key role, such as:
- Sportswear and activewear
- Winter clothing
- Protective medical textiles (e.g., masks and gowns)
- Industrial filters
Common Air Permeability Test Units
The air permeability test unit varies depending on the testing standard and region. Common units include:
- cm³/cm²/s
- Represents the volume of air (in cubic centimeters) passing through one square centimeter of fabric per second.
- Widely used in ISO and ASTM standards.
- L/m²/s
- Expresses the volume of air (in liters) passing through one square meter of fabric per second.
- Common in European standards.
- cfm (cubic feet per minute)
- Indicates the volume of air (in cubic feet) passing through a specific area (usually one square foot) per minute.
- Popular in the U.S., especially in technical and industrial applications.
- m³/m²/min
- Measures the airflow in cubic meters per square meter per minute, often used in filter testing.
Understanding the Air Permeability Formula
The Air permeability formula helps calculate the rate of air passage through a fabric under defined conditions. It is represented as:
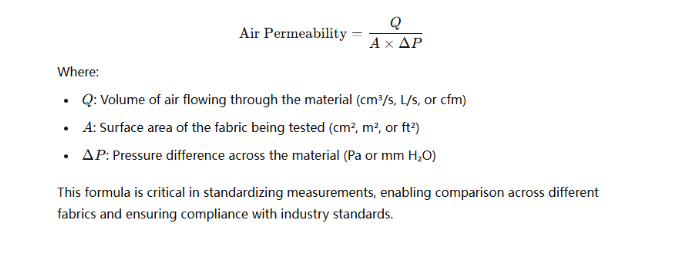
This formula is critical in standardizing measurements, enabling comparison across different fabrics, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Standards Governing Air Permeability Testing
The use of consistent air permeability test units and formulas is ensured by international standards, including:
- ISO 9237
- Specifies the method for determining air permeability in woven, knitted, and nonwoven fabrics. Results are expressed in cm³/cm²/s or L/m²/s.
- ASTM D737
- A widely adopted standard in North America, is measuring air permeability in cfm for textiles under specific pressure differentials.
- DIN 53887
- Common in Europe for technical textiles, with results often expressed in L/m²/s.
- EN 14683 (Medical Textiles)
- Focuses on air permeability testing for surgical masks, ensuring both breathability and barrier effectiveness.
Importance of Air Permeability Test Units
- Quality Control
- Uniform test units help manufacturers monitor consistency in fabric production, ensuring high-quality products.
- Application-Specific Insights
- Different applications require tailored airflow characteristics. For instance:
- High air permeability is crucial for sportswear to enhance ventilation.
- Low air permeability is vital for windproof jackets and filters.
- Different applications require tailored airflow characteristics. For instance:
- Standardized Comparisons
- Using a common air permeability test unit allows global manufacturers to compare results, regardless of regional testing standards.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Compliance with standards like ISO or ASTM ensures products meet market and consumer expectations.
Factors Affecting Air Permeability Test Results
The air permeability of a fabric depends on several factors, which influence the test results and their corresponding units:
- Fabric Construction
- Open-weave or knitted fabrics have higher air permeability due to larger pore sizes.
- Densely woven fabrics or laminated materials restrict airflow, leading to lower permeability.
- Fabric Thickness
- Thicker fabrics impede airflow, reducing air permeability values.
- Fiber Type
- Natural fibers like cotton generally allow more air passage compared to synthetic materials like polyester.
- Finishing Treatments
- Coatings, laminations, or water-repellent treatments block air passages and reduce permeability.
Applications of Air Permeability Testing
The use of air permeability testing and accurate air permeability test units spans various industries:
- Apparel and Sportswear
- Determines breathability in garments designed for active use or hot climates.
- Medical Textiles
- Ensures surgical masks and gowns strike the right balance between breathability and protective performance.
- Technical and Industrial Textiles
- Evaluates filters, parachutes, and tents to ensure optimal airflow control.
- Home Textiles
- Tests fabrics used in curtains, upholstery, and bedding to balance comfort and functionality.
Recent Advances in Air Permeability Testing
- Automated Testing Devices
- Modern machines provide faster, more accurate readings while minimizing human error.
- Devices like the FX 3300 Air Permeability Tester can automatically display results in multiple test units, such as L/m²/s or cfm.
- AI and Machine Learning
- AI-based systems predict air permeability based on fabric structure and material composition, reducing the need for repetitive testing.
- Sustainable Testing Methods
- New eco-friendly textiles require innovative air permeability testing methods to ensure performance without compromising sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Understanding the air permeability test unit is fundamental for analyzing fabric performance and ensuring products meet specific application needs. Whether expressed in cm³/cm²/s, L/m²/s, or cfm, test units provide valuable insights into textiles’ breathability, comfort, and functionality. When combined with the air permeability formula, they enable manufacturers to evaluate materials consistently, comply with global standards, and create superior products.
As industries continue to innovate with advanced textiles, the importance of air permeability testing will only grow, supporting the development of breathable, high-performance fabrics for diverse applications.
